Submissions






GlyTouCan
Glycan Structure Repository
GlyComb
Glycoconjugate Repository
GlycoPOST
Glycomics MS raw data RepositoryUniCarb-DR
Glycomics MS Repository for glycan annotations from GlycoWorkbench
LM-GlycoRepo
Repository for lectin-assisted multimodality dataAll Resources
Genes / Proteins / Lipids Glycans / Glycoconjugates Glycomes Pathways / Interactions / Diseases / OrganismsTools
Guidelines
MIRAGE
 Major prion protein
Major prion protein
Summary
- UniProt ID
- P04925
- Gene Symbol
-
- Prn-p
- Prnp
- Prp
- Gene ID
- 19122
- Organism
- Mus musculus (house mouse)
External Links
- GlycoProtDB
- GPDB0003279
- GlyConnect
- GlyGen
- P04925
- PubChem
- P04925
- RaftProt
- P04925
- Re-Glyco
- P04925
Annotation
- Keyword
-
- 3D-structure
- Cell membrane
- Copper
- Direct protein sequencing
- Disulfide bond
- GPI-anchor
- Golgi apparatus
- Hydroxylation
- Metal-binding
- Prion
- Reference proteome
- Repeat
- Signal
- Zinc
- Gene Ontology (GO)
| GO Term |
|---|
| endoplasmic reticulum |
| Golgi apparatus |
| cytosol |
| cell surface |
| side of membrane |
| postsynaptic density |
| terminal bouton |
| membrane raft |
| plasma membrane |
| membrane |
Sequence
MANLGYWLLALFVTMWTDVGLCKKRPKPGGWNTGGSRYPGQGSPGGNRYPPQGGTWGQPHGGGWGQPHGGSWGQPHGGSWGQPHGGGWGQGGGTHNQWNKPSKPKTNLKHVAGAAAAGAVVGGLGGYMLGSAMSRPMIHFGNDWEDRYYRENMYRYPNQVYYRPVDQYSNQNNFVHDCVNITIKQHTVTTTTKGENFTETDVKMMERVVEQMCVTQYQKESQAYYDGRRSSSTVLFSSPPVILLISFLIFLIVG
Glycosylation Sites
| Position | Description | PubMed ID | GlyTouCan ID | Source |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 180 | N-linked (GlcNAc...) asparagine | |||
| 196 | N-linked (GlcNAc...) asparagine |
Feature
 : Glycosylation Site from GlyGen
: Glycosylation Site from GlyGen : Glycosylation Site from UniProt
: Glycosylation Site from UniProt
Pathway
| Pathway Name | Organism |
|---|---|
| Insertion of tail-anchored proteins into the endoplasmic reticulum membrane | Mus musculus |
Disease
| DO ID | Disease Name | Source |
|---|---|---|
| DOID:0050433 | fatal familial insomnia | |
| DOID:11949 | Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease | |
| DOID:4249 | Gerstmann-Straussler-Scheinker syndrome |
 G60967DT
G60967DT
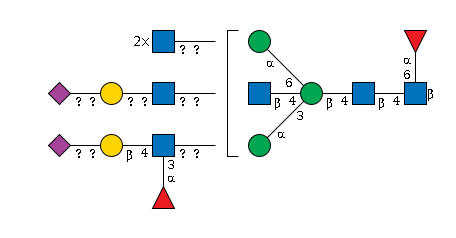 G39945EK
G39945EK
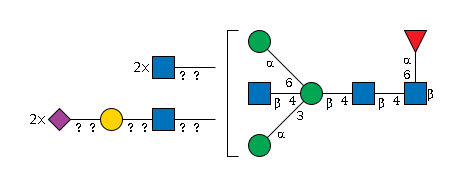 G90443NH
G90443NH
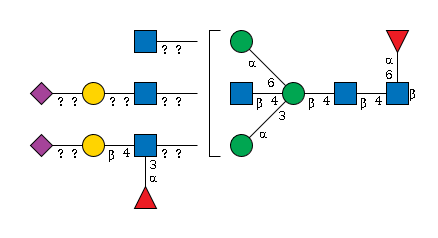 G25180HQ
G25180HQ
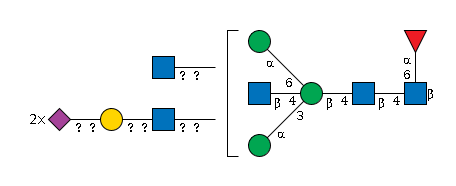 G26014MK
G26014MK
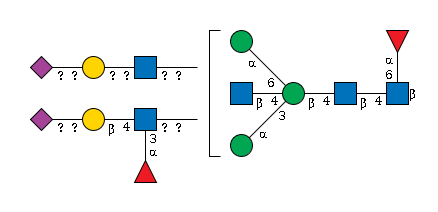 G76519VT
G76519VT
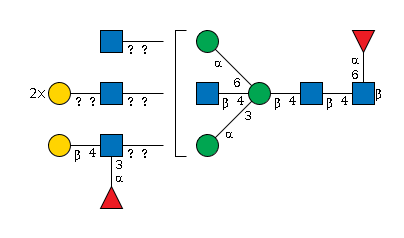 G91623TN
G91623TN
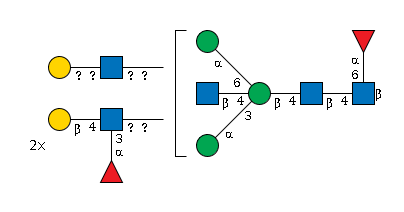 G99035PG
G99035PG
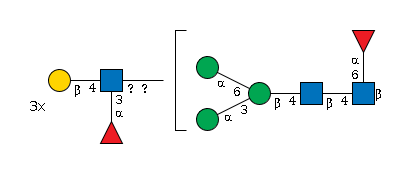 G32671AN
G32671AN
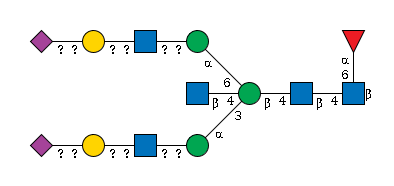 G65219TP
G65219TP
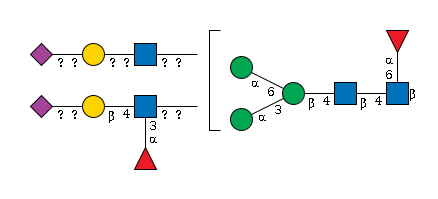 G71071YT
G71071YT
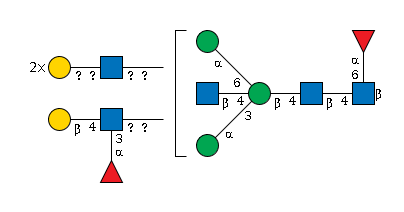 G26896YH
G26896YH
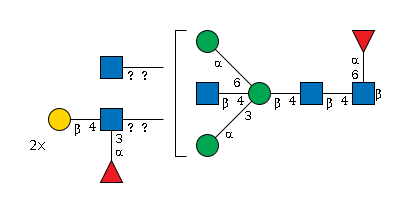 G94373HA
G94373HA
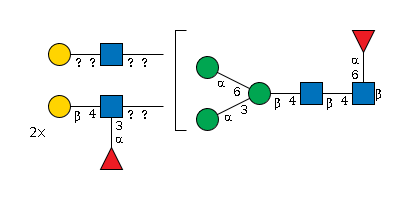 G24132CP
G24132CP
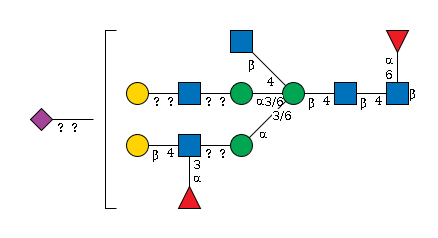 G82138AT
G82138AT
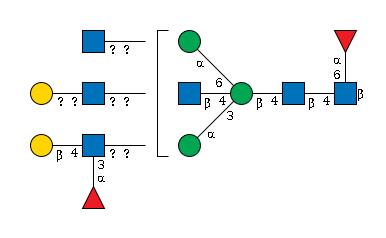 G62837IG
G62837IG
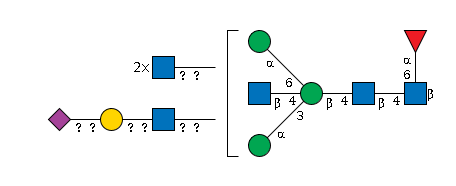 G19099PA
G19099PA
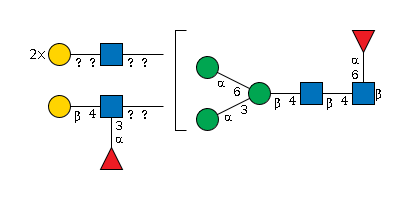 G52003QG
G52003QG
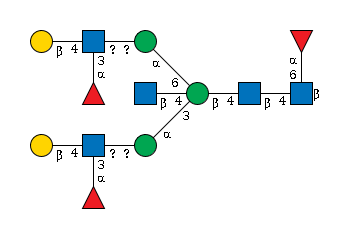 G94163JU
G94163JU
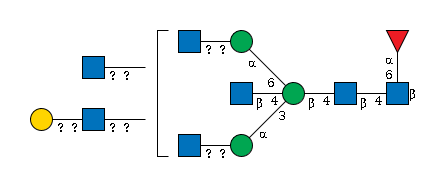 G65365UP
G65365UP
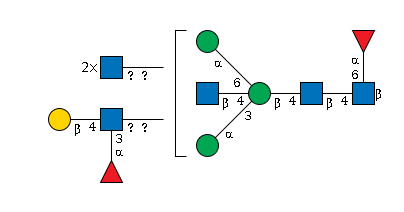 G26371XR
G26371XR
 G35687VS
G35687VS
 G29895JE
G29895JE
 G07682PQ
G07682PQ
 G45045RU
G45045RU
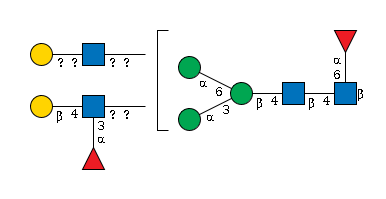 G15791TK
G15791TK
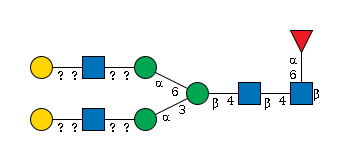 G57818FI
G57818FI
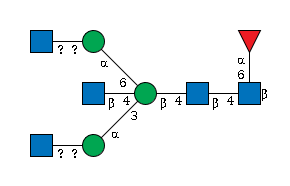 G92129PT
G92129PT
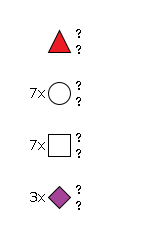 G41205CB
G41205CB
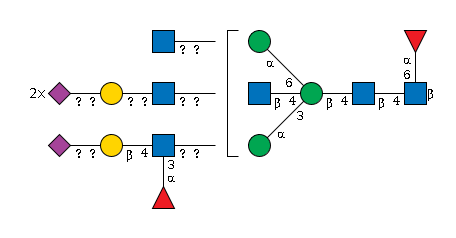 G43549OX
G43549OX
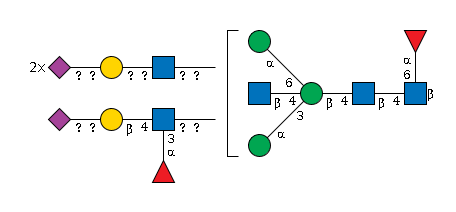 G43953LS
G43953LS
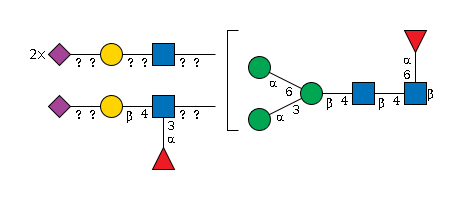 G05395FV
G05395FV
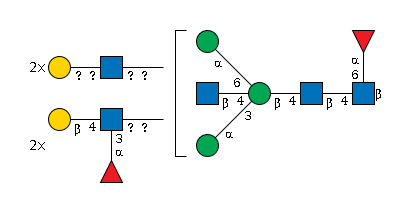 G29721UX
G29721UX
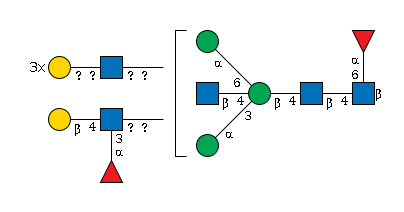 G63046OH
G63046OH
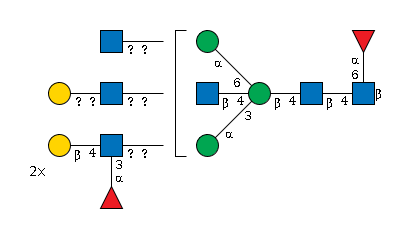 G33785ND
G33785ND
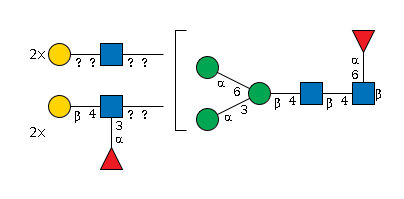 G74320MK
G74320MK
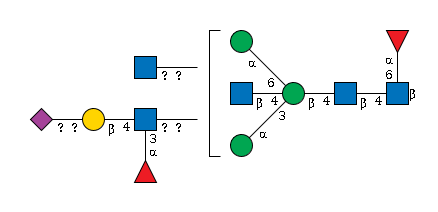 G40012WS
G40012WS
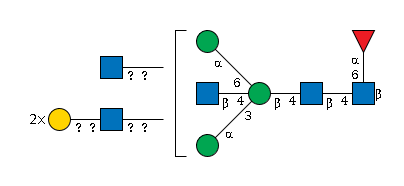 G22137OG
G22137OG
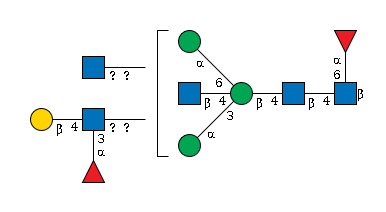 G65550TC
G65550TC
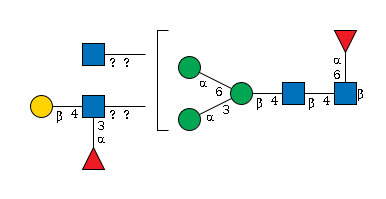 G25495RY
G25495RY
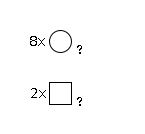 G64527OM
G64527OM
 G05724UK
G05724UK
 G74724QE
G74724QE
